Eye Stye: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Understanding Eye Styes
If you have ever had a sore, red lump appear along your eyelid, you may have experienced an eye stye. Styes are a common eye condition and, while uncomfortable, they are usually harmless and temporary. They can make blinking painful, cause swelling around the eye, and be frustrating to deal with — especially when they appear suddenly.
Understanding what an eye stye is, what causes it, and how it develops can help you manage symptoms properly and reduce the chance of it coming back.
What Is a Stye?
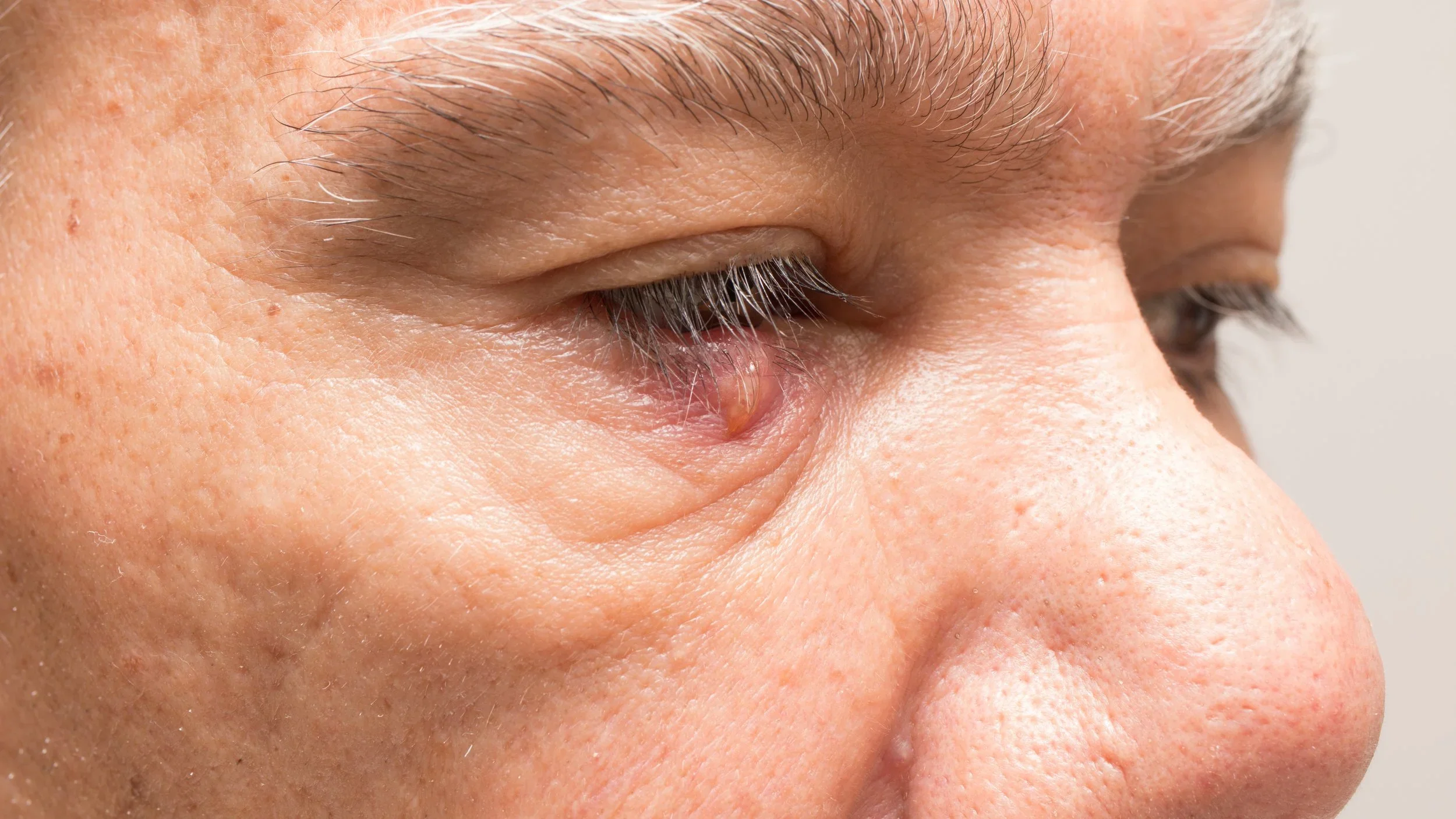
An eye stye, also known medically as a hordeolum, is an infection of a small oil gland in the eyelid. These oil glands sit along the eyelid margin and help keep the surface of the eye lubricated. When one of these glands becomes blocked and infected with bacteria, a stye can form.
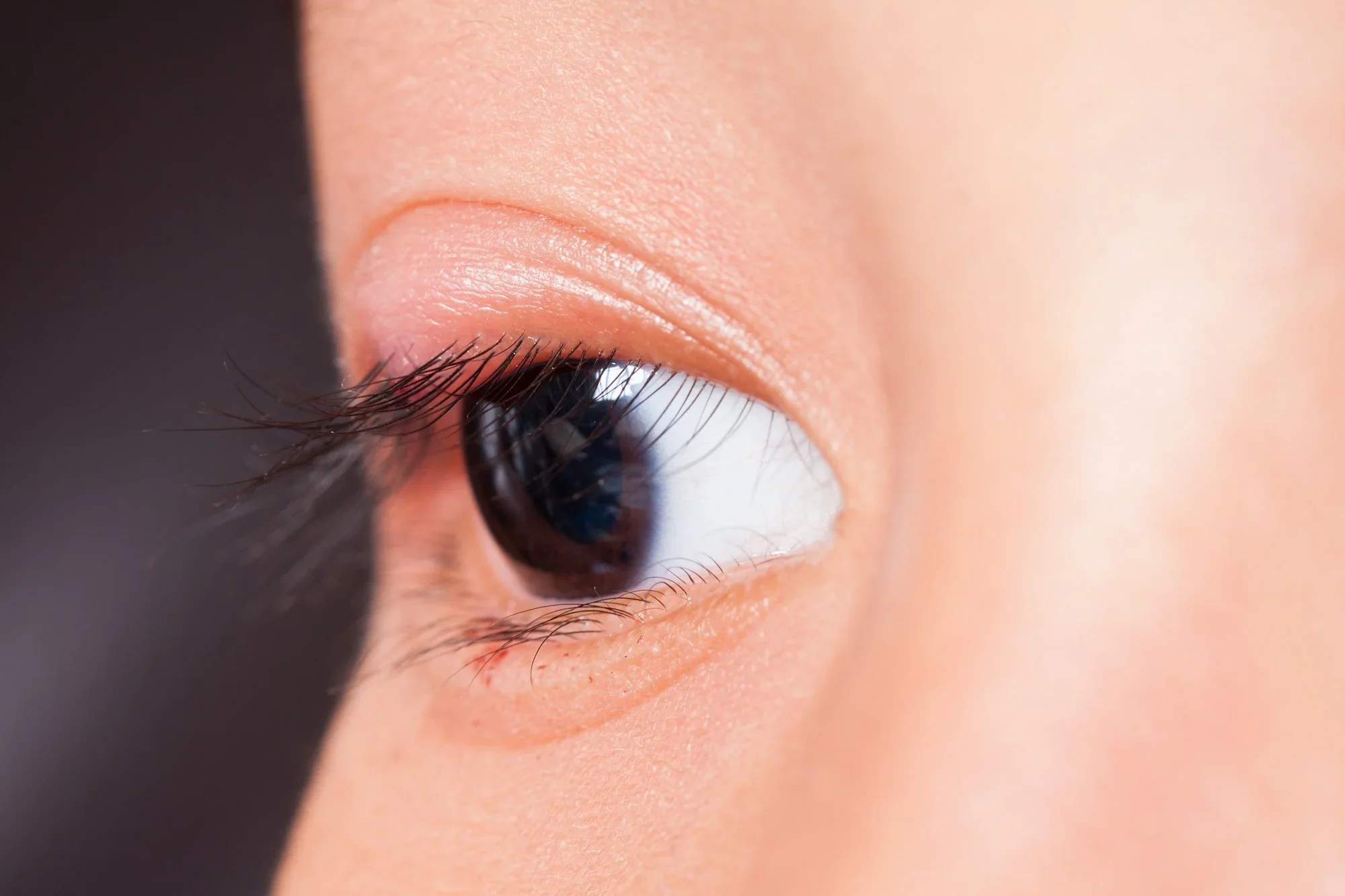
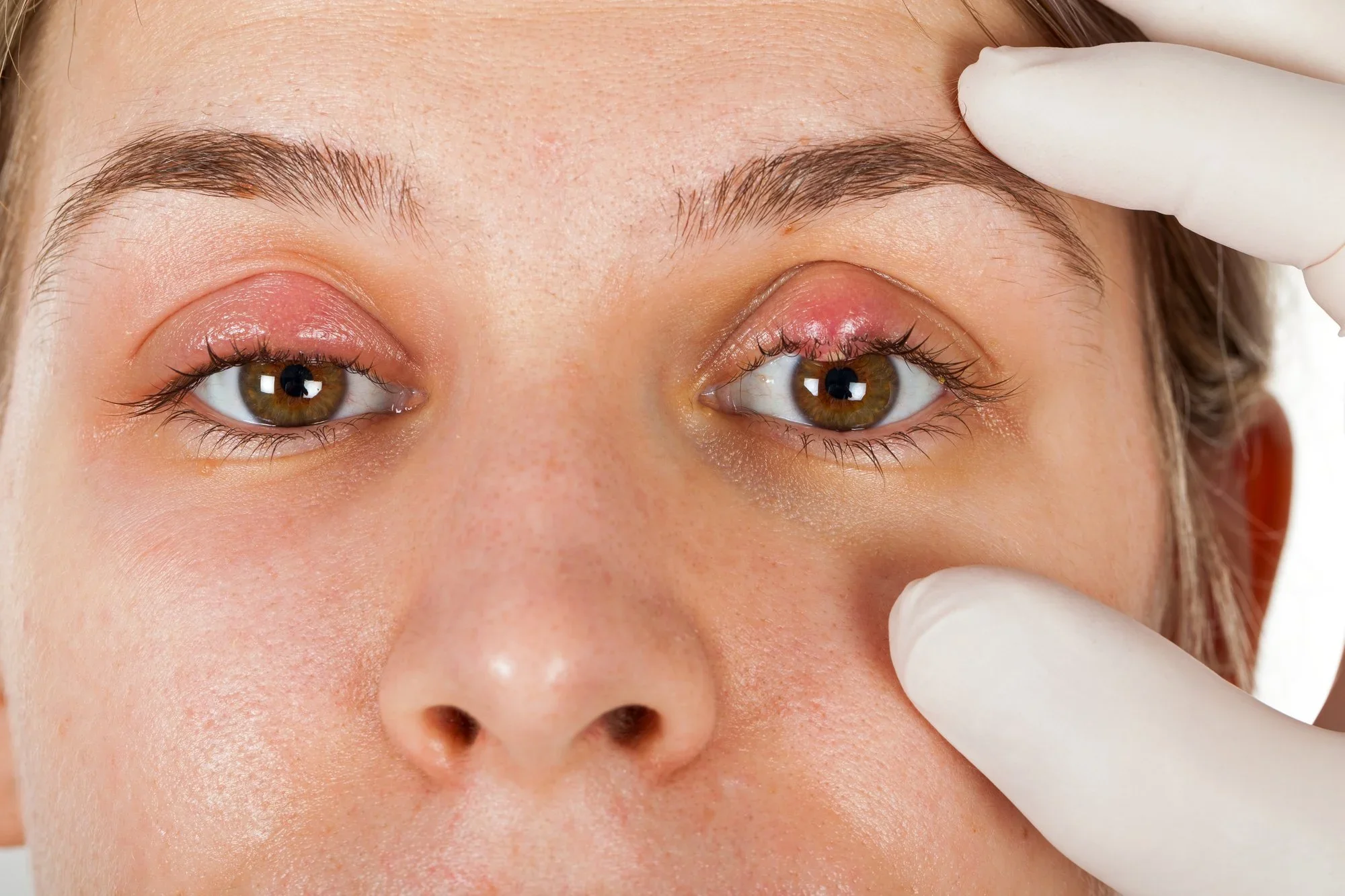
A stye usually appears as a red, swollen bump on the upper or lower eyelid. It may look similar to a pimple and is often tender or painful to touch. Some styes develop on the outer edge of the eyelid near the eyelashes, while others form slightly deeper inside the lid.
Although styes can look concerning, most clear up on their own with simple care and do not cause long-term damage to the eye.
Stye vs Chalazion: What’s the Difference?
Styes are sometimes confused with chalazia, another type of eyelid lump. While they may look similar, they are not the same condition.
A stye:
Is caused by a bacterial infection
Is usually painful or tender
Develops quickly and may have a yellow centre
A chalazion:
Is caused by a blocked oil gland without infection
Is usually painless
Develops slowly and can last longer
Knowing the difference matters, as chalazia may require different management if they do not resolve on their own.
What Causes Styes?
Styes are most commonly caused by bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus, which naturally live on the skin. Problems occur when these bacteria enter a blocked oil gland along the eyelid.
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing a stye, including:
Poor eyelid hygiene
Touching or rubbing the eyes with unwashed hands
Blocked oil glands along the eyelid
Using old or contaminated eye makeup
Incomplete makeup removal
Chronic eyelid inflammation (blepharitis)
Stress, fatigue, or lowered immunity
When oil glands do not drain properly, bacteria can multiply inside the gland, leading to swelling, redness, and infection.
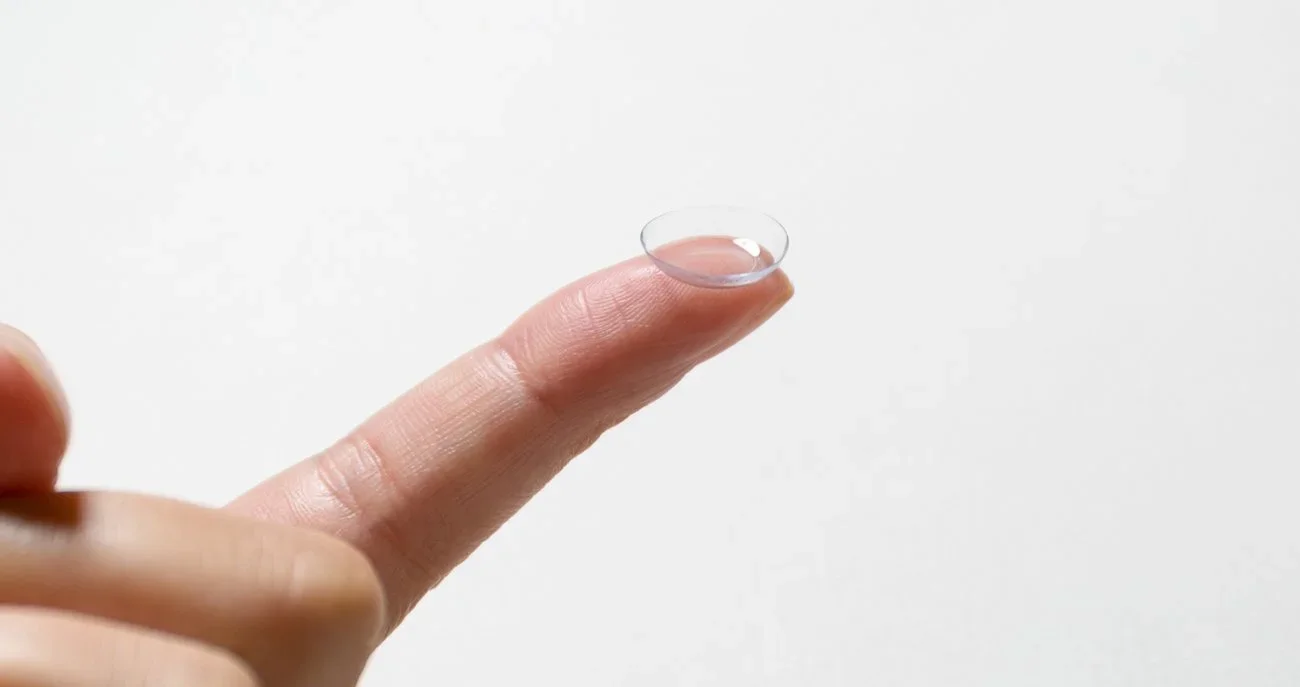
Can Contact Lenses Cause Styes?
Contact lenses do not directly cause styes, but improper contact lens care can increase the risk.
Handling lenses without washing your hands, wearing lenses longer than recommended, or failing to clean and replace lenses and cases properly can allow bacteria to build up around the eyelids. This makes it easier for bacteria to enter blocked oil glands and trigger a stye.
If you wear contact lenses and develop a stye, switching to glasses temporarily can help reduce irritation while the eyelid heals.
Common Symptoms of an Eye Stye
Symptoms of a stye often develop gradually and may include:
A red, swollen lump on the eyelid
Pain or tenderness around the affected area
Swelling of part or all of the eyelid
A gritty or irritated feeling in the eye
Watery eyes
Crusting along the eyelashes
Mild blurred vision due to swelling
Some styes may develop a small yellow or white centre as the infection progresses. This does not mean the stye should be squeezed or popped.
How to Get Rid of a Stye
Most eye styes improve on their own within 7 to 10 days, especially with proper self-care. Treatment focuses on easing discomfort, reducing swelling, and encouraging natural drainage.
Stye Self-Care
The most effective and widely recommended self-care method for a stye is applying a warm compress.
How to Use a Warm Compress
Soak a clean cloth in warm (not hot) water
Wring it out and place it gently over your closed eye
Leave it in place for 10 to 15 minutes
Re-warm the cloth as needed to maintain warmth
Repeat 2 to 4 times a day
Warmth helps soften blocked oils in the eyelid and encourages the gland to drain naturally. After warming, gentle eyelid massage may help, but pressure should always be light.
Avoid squeezing or popping a stye, as this can worsen the infection and increase the risk of complications.
Home Remedies: What to Be Careful With
Some people try home remedies such as tea bags or natural products to reduce irritation. While warmth can be helpful, not all home remedies are safe for the eyes.
Strong substances such as undiluted vinegar or essential oils should not be applied near the eye, as they can cause irritation or damage. If symptoms worsen or do not improve, it is best to seek professional advice rather than experimenting with unproven remedies.
Medical Treatment Options
Most styes do not require medical treatment. However, professional care may be needed if:
The stye does not improve after 7–10 days
Pain or swelling worsens
Vision becomes affected
The infection spreads
In these cases, a healthcare professional may recommend:
Antibiotic ointment or drops
Further eyelid treatment
Minor drainage in persistent cases
According to Australian health guidance, antibiotics are not routinely required for uncomplicated styes, as most resolve naturally with good hygiene and warm compresses.
How to Prevent a Stye
Good hygiene plays a key role in preventing styes, especially for people who experience them repeatedly.
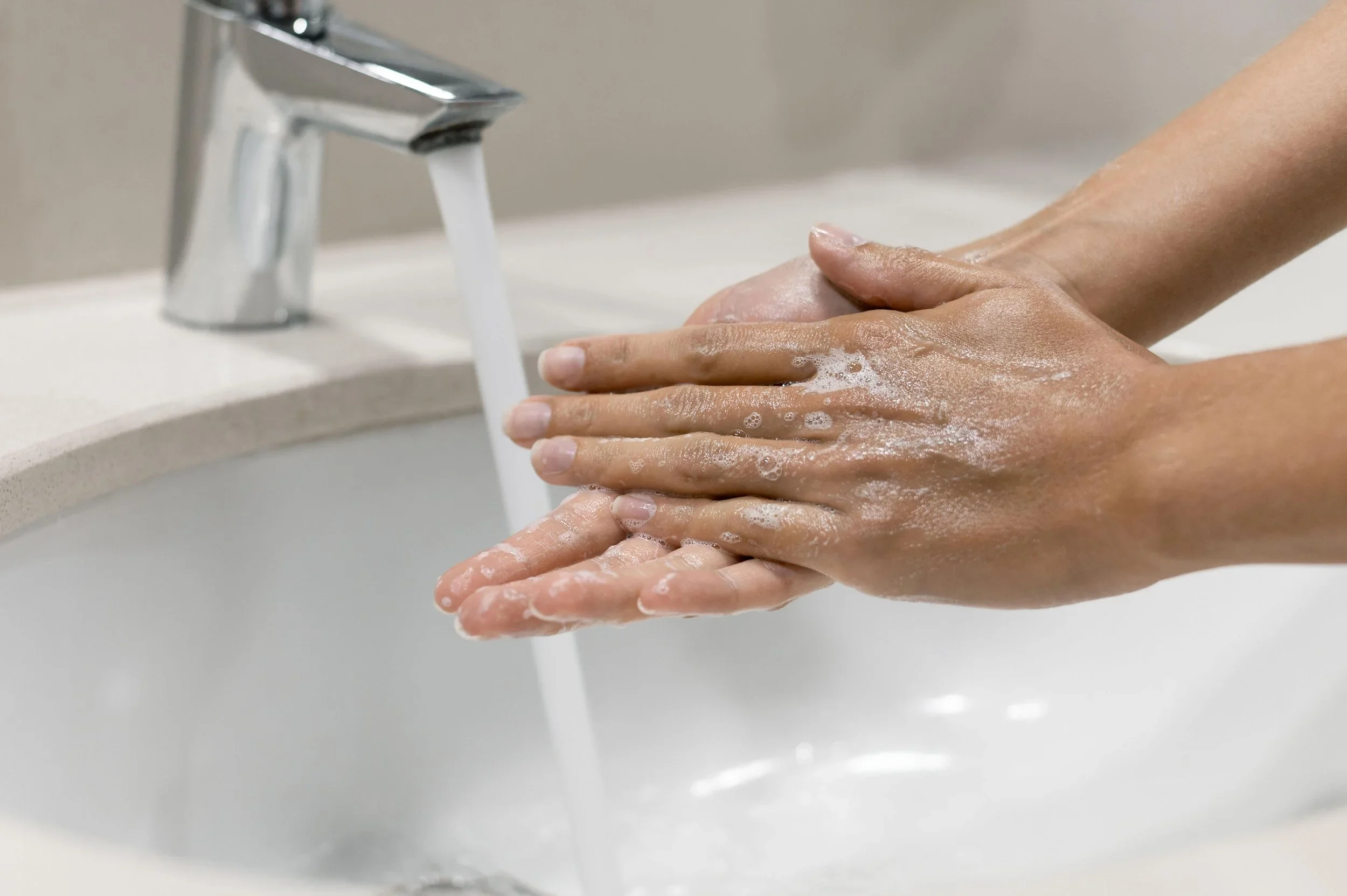
Maintain Good Eyelid Hygiene
Wash hands regularly
Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes
Remove eye makeup thoroughly each night
Replace eye makeup every 3–6 months
Proper Contact Lens Care
Wash hands before handling lenses
Clean and store lenses as directed
Replace lens cases regularly
Avoid sleeping or swimming in lenses unless advised
Support Overall Eye Health
Get adequate sleep
Manage stress levels
Maintain a balanced diet
Wearing glasses instead of contact lenses during times of irritation can also reduce the risk of developing a stye.
When to Seek Medical Attention
You should seek professional advice if:
The stye does not improve within two weeks
Pain becomes severe
Swelling spreads beyond the eyelid
Vision changes occur
You experience recurring styes
Early assessment can help rule out other conditions and prevent complications.
Stye FAQs
Are styes contagious?
No. Styes are not contagious, but bacteria can spread through shared towels, makeup, or pillowcases.
How long does a stye last?
Most styes clear within 7 to 10 days, though some may last slightly longer.
Can I pop a stye?
No. Popping a stye can spread infection and cause scarring.
Is it okay to leave a stye alone?
Yes, as long as it is kept clean and monitored for changes.
What makes a stye worse?
Lack of sleep, eye rubbing, dirty makeup, excessive contact lens wear, and poor hygiene can all worsen a stye.
Conclusion
Eye styes are a common and usually temporary eyelid condition. While they can be uncomfortable and inconvenient, most improve with simple self-care such as warm compresses and good hygiene. Understanding what causes a stye and how to manage it properly can help ease symptoms and reduce the risk of recurrence.
If a stye becomes persistent, painful, or begins to affect vision, seeking professional advice is important. With the right care, most styes resolve without long-term effects, allowing your eyes to return to comfort and health.